What is Company Data? Examples, Providers & Datasets to Buy

- Overview
- Datasets
- Providers
- Use Cases
- Attributes
- Guide
- FAQ
- Overview
- Datasets
- Providers
- Use Cases
- Attributes
- Guide
- FAQ
What is Company Data?
Company data comprises information that offers insight into a company’s characteristics and performance, including financial statements, sales figures, customer information, employee records, and market research data. It’s used for analyzing company performance, market research, and identifying potential business opportunities.
What Are Examples of Company Data?
Examples of company data include datasets offering comprehensive insights into business operations and profiles. Key examples include:
- Company Profiles: Names, addresses, and contact details of businesses.
- Industry Classification: SIC, NAICS, or custom categories for industries.
- Financial Data: Revenue, expenses, and profitability metrics.
- Ownership and Leadership: Information about executives, founders, and stakeholders.
- Employee Data: Number of employees and workforce distribution.
Editor's Pick
Featured datasets

Company Data | 6.7MM+ Total Companies | Company Name, Industry, Employees, Revenue, Website, Addresses + More

Coresignal | Company Data | Firmographic Data | Global / 102M+ Records / Largest Professional Network + Owler + 9 Other Sources / Updated Monthly

Success.ai | B2B Company & Contact Data – 28M Verified Company Profiles - Global - Best Price Guarantee & 99% Data Accuracy
Best Company Databases, Datasets & API
The best company datasets provide detailed insights into business profiles, financial performance, and industry classifications. This curated list features the top company datasets and APIs, selected for accuracy, quality, and trusted providers where you can buy company data.

Company Data | Global Coverage | 65M+ Company profiles | Bi-weekly updates

Company Data | 28M Verified Company Data Profiles | Best Price Guarantee

Factori US Company Data | B2B Leads Data | Company API | B2B Company Search API | 6M+ records| Updated monthly

WebAutomation | Global Firmographic Data | Company Data/ 15M+ Company Records/ Cruchbase + 5 Other Sources | Monthly Updates | Historical Data

LinkedIn Company Data – US Business Profiles with Google Maps Validation LinkedIn Company Data for BI, Company Analysis & Portfolio Monitoring

B2B Company Data | 2.1M US Business Operations | Verified Safe to Email

Company Data | Firmographic Data | 16+ Industry Segmentation | Global Coverage | 100M+ Contacts | (Verified E-mail, Direct Dails)| 20+ Attributes

Company Data | Business Location Data | Company Details for Global POIs

CompanyData.com (BoldData) - Healthcare Company Data (2.5M Companies)

Crunchbase Companies List | Crunchbase Company Database | Crunchbase Startups List | 3Million+ Records
Can't find the data you're looking for?
Let data providers come to you by posting your request
Post your request
Top Company Data Providers & Companies
Popular Use Cases for Company Data
Company data can be employed by your business in more ways than one. As mentioned in the previous section, there are a lot of departments of your business that are going to benefit from the company data. Therefore, it should be used to its full potential to make the best out of your marketing and sales campaigns.
Here are the few ways in which you can use company data:
Account Based Marketing
Company data can come in very handy in all stages of ABM, from identifying a new account, to nurturing it, to closing the deal.
Identifying New Accounts
Analyzing company data to evaluate your key clients can inform you about the key things you should be offering when looking to acquire a new account. For example, you can find when the right time to reach out might be by using intent data, and find a good point of contact via contact data. This can help you properly nurture the new account and prepare it to close the deal with the sales team.
Lead Scoring and Prioritization
There are countless companies that will qualify as a potential prospect, but they’re not always all a priority. Company data not only allows you to identify these companies, but it also helps you to filter them in terms of when is the best opportunity to seal the deal.
For example, firmographic data can show the expected length of a company’s sales cycle and this can help to better prepare your sales team.
In other cases, many businesses prefer their clients to be in close proximity to them. A company database can help you to filter the companies by their locations. You might just find the perfect fit right around the corner!
Personalizing Communication
After you’ve found a client account that is interested, nurtured them and identified when they are interested, the final step is then ensuring you engage with them in terms that they relate to. Company data can help your sales teams to speak in the right way and deliver the right message to the account of interest, which is especially vital when securing the final part of the deal-making process.
Company Data Analysis
Analysis is, arguably, the one of the most key uses of collected company data. The data alone means very little. It is only with analysis that the data holds value to you and your business.
Descriptive Analysis
Descriptive analysis provides you with an overview of what the company of interest is and how they perform. This shows you the current and past situation of the company, and is primarily based on firmographic, technographic and intent data. Descriptive analysis includes the process of looking at past data to identify trends.
Predictive Analysis
Predictive analysis will help you in preparing for future trends by analyzing the growth rate of a company and its revenue charts. These can be helpful in adjusting your marketing strategies likewise.
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis takes the aforementioned predictions and suggests actions. In other words, it is about handling the various situations anticipated by predictive analysis. For example, if predictive analysis talks about opportunities for your business to sell a product in a new market, the prescriptive analysis will talk about how your salesperson can pitch it.
Key Attributes of Company Data
The key attributes of company data can be divided into firmographic and technographic-based data. Depending on what type of information about a company you require, you will rely more on one or the other of these two. With the use of these two types of data you can build an extensive company contact database of those companies most suited to fulfilling your company’s needs.
In general, company data will have the following attributes:
Firmographic Attributes
Firmographic data is data specific to an organisation. Just as demographic data focuses on individuals, firmographic data focuses on the organisation. B2B businesses can use firmographic data to help with market segmentation by using variables to categorise firms. Firmographic data can tell us which industry an organisation fits in to or its location, for example.
Company Name and Address
The most basic data on a company you could have! It goes without saying that you need to know the name of the company you’re engaging with. Along with that, it’s helpful to have the address of the head office of the company, as well as the addresses of their branches in any countries you’re interested in. By having access to a company’s address or addresses, you can make informed assumptions about their behaviours, whether they be influenced by the geography, climate or regulations of the area.
Industry
When using firmographic segmentation to categorise firms, firms can be attributed an industry label. This indicates the firm’s primary activities, whether that be the type of services they offer or the products that they produce. When trying to target a particular firm it is crucial that you take into account which industry they operate in. For example, a company that operates in the environmental sector is unlikely to be seeking the same resources as a company that operates in the high-street fashion industry. Not only is it important to take industry labels into account to ensure the appropriate resources are delivered to those firms, but also to help you to sift out those firms that are not involved in the particular industry you are looking to work with. For this reason, it’s a good idea to include industry in your B2B ICP before you make a data purchase. There’s no point investing in an IT company database if you’re targeting retailers!
Company Size and Revenue
Company size is typically divided into two attributes: annual revenue and number of employees.
A company’s revenue is a key consideration in firmographic segmentation. It is little use targeting a company that doesn’t have the funds to afford what you’re offering. For this reason, it’s good to build a customer ICP so you know what kind of company you’re looking to prospect with data-driven outreach. If it’s large companies and enterprises, you’ll need to buy corporate data. If your ICP is a start-up or SME, you can buy start-up company data.
Taking into consideration factors such as whether a company has experienced considerable fluctuations is their revenue over the years or where they fall in terms of being a small start-up or whether they’re listed on the FTSE 100 helps you adapt your B2B marketing strategies. A company revenue database gives you a comprehensive source of truth for revenue and how it’s fluctuating, which is why revenue data is such an important company data attribute.
Having data indicating the number of employees a company has is one of the most helpful pieces of firmographic data you can have. The number of employees indicates whether they’re a small start-up, medium sized company, or even a large multinational company. Ultimately, these numbers will greatly influence how you go about targeting these companies. The way you would approach a small, local business is completely different to how you would a large business with bases in multiple countries.
Employee Information
You can also expect the company database to delve into employee information in detail. This data generally consists of the names of the employees, along with their role in the company. It should also include the department of the employee and their seniority. Being aware of individual employees and their roles helps you to gain an impression of who best to contact and target within the company.
Products
One type of firmographic data that is often provided when purchasing company data is information on the various products and services offered by the company, both those currently being offered and past ventures of the company. This can help with finding potential cooperation and for performing product analysis. If you can detect an overlap of your products or services with another company or observe that they are offering something your company is lacking this can provide great potential for collaboration.
Funding Information
It is also possible to discover information on a company’s current level and sources of funding, as well as to get an idea of their potential budgets. Funding information can give you a clearer idea about the growth of the company and when and how it might spend its finances. If a company is heavily reliant on one source of funding you might wish to take this into account before targeting that company. A company reliant on one source of funding, particularly a source that might be vulnerable to fluctuations or losses, may not have a very stable or secure future, making it a company that may prove to present future financial difficulties.
Legal Status
Another attribute that can be used in firmographic segmentation is a company’s legal status. For example, a company could be operating as a Public Limited Company (PLC), a privately held company, a Limited Liability Corporation (LLC) or a partnership, just to name a few. Being aware of the legal status of a company is of importance, whether you’re looking to invest in the company or target your marketing towards them.
Technographic Attributes
Technology Stack
Having access to data on a company’s current technology stack allows you to build up a profile of that company and how they operate. You should also expect to be presented with when these technologies were acquired, helping to form a timeline for this profile. When it comes to technographic segmentation, there is often an element of assumption: a company may rely on a certain software, leading you to draw conclusions about the company’s operational methods. These conclusions, however, are more often that not, very accurate if you have an understanding of either the technologies used or an understanding of how companies of that size or in that industry generally operate.
Online Presence and Social Profiles
Almost every company nowadays dedicates time to maintaining its public presence through blogs and various social media profiles. Company data effortlessly collects and summarises information from these platforms for you. As well as this, it can offer an insight into how a company behaves online, including specific social media posts, job postings, and online searches.
This information can add context into how the company functions and wishes to present itself. Collecting information from social media profiles or blogs is reasonably easy to do and, as companies turn to these platforms more and more, they present an increasingly relevant source of information about a company and its behaviours.
Intent Data Attributes
Buying Signals
In-depth company data may include information on the company’s more recent acquisitions and services the company has recently stopped using. It could also even contain information on what the company has been searching for online or on comparison sites.
Below, we outline the most popular attributes associated with this type of data—features that data buyers are actively seeking to meet their needs.
| Attribute | Type | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| String | The name of a company or business, might be the legal or brand name. | View 546 datasets | |
| String | The last name (surname) of a contact. | View 468 datasets | |
| String | The first name of a contact. | View 464 datasets | |
| String | The name of a country. | View 418 datasets | |
| String | The approx. number of employees working for a company. | View 397 datasets | |
| String | The email address of a company or contact. | View 355 datasets |
Sources and Collection Methods of Company Data
Because it incorporates many overlapping data types, it’s difficult to get all company data from one place. Indeed, most company datasets are compiled from many sources. These include whitepapers, company registries, company social media posts, company webpage source codes, and phone calls.
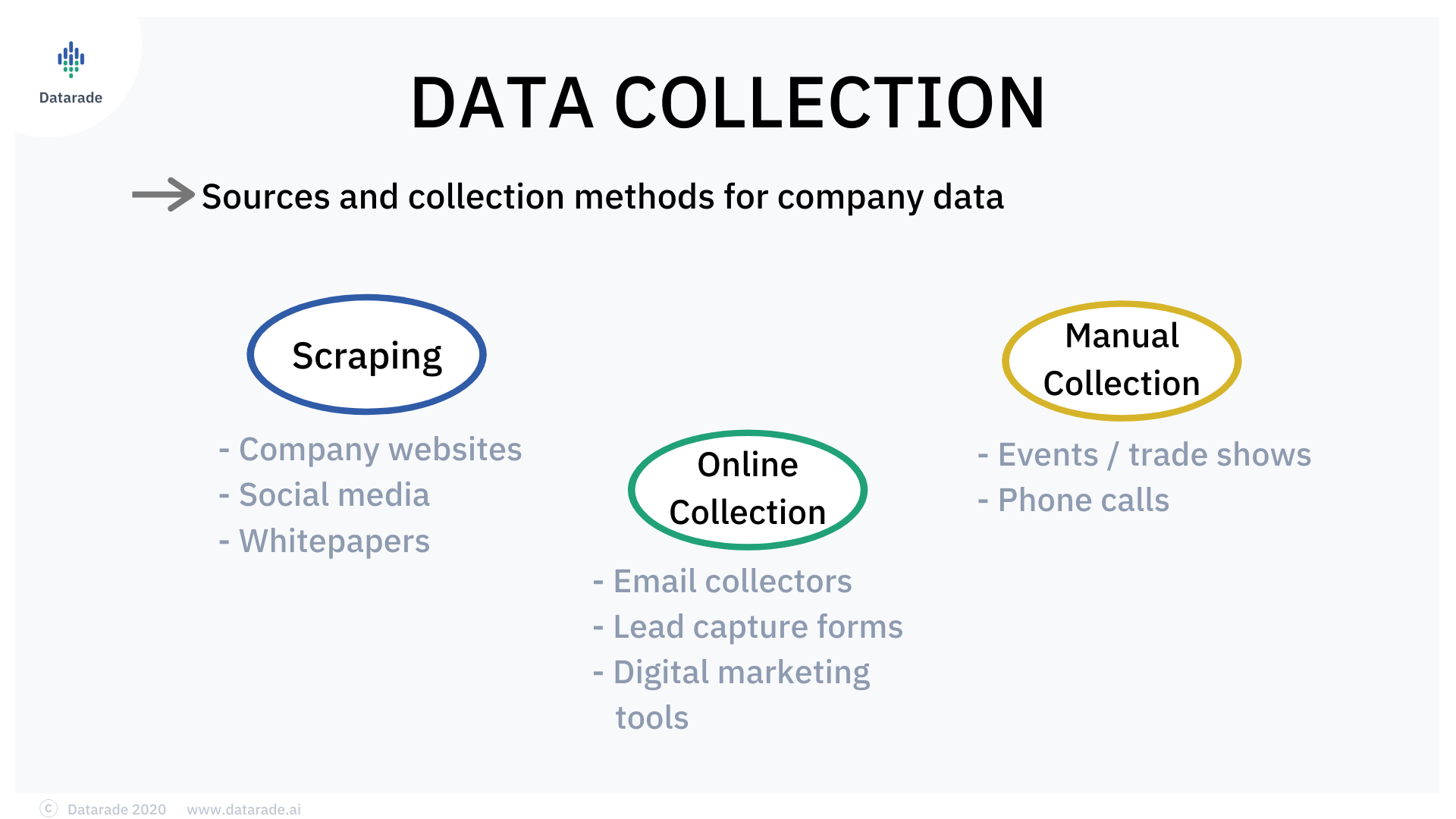
Due to the comprehensive nature of company data, collecting it alone is a massive investment of time and resources. For this reason, many organizations turn to third-party data providers to collect company data on their behalf.
Here’s some of the most common sources for company data sorted by their collection methods.
Scraping
Scraping is the extraction of relevant data from a source, such as a website or document. This extraction is usually performed by a computer programme. This software is able to identify any important or relevant data and retrieve it for the company to put to use to inform them about that targeted company. In some cases, scraping allowed you to collect code from a website, indicating which technologies a company is using. It is more likely that you will be able to collect this data if the prospective company is using marketing automation software because it is often the case that the website’s source code presents evidence of it.
Whitepaper Downloads
The whitepapers published by a company or an external party not only have the description of the company’s products and services, but they also contain details about the company itself.
These whitepapers can be a good way of finding out in-depth information about the company, including, potentially, their funding information and the names of the important company members. Very often, the size of a company can also be found in these whitepapers.
The best part about this collection method is that the information provided here is completely accurate. However, this source of database collection does not provide all the attributes needed for compiling the company database. Moreover, whitepapers are not published very frequently, so unless they are regularly updated, their information can be somewhat out of date.
Industry Reports
You can expect a company to publish reports, roughly every quarter, about the company’s net growth and revenue. These reports can be very helpful in collecting financial information about the company.
These reports offer accuracy, but like with whitepapers, they only offer information about selected fields and it is likely that, only shortly after publishing, the information is outdated and, therefore, not entirely accurate.
Webinar Registrations
Webinar registrations are a good way of finding out detailed information about a company’s employees and interested customers. It combines the high accuracy of methods such as event registrations, without requiring the hard labour and effort needed for the physical collection methods.
Social Media Activity
Social media platforms such as LinkedIn and Facebook offer a great way to gather company data. Platforms such as LinkedIn are growing increasingly popular among professionals and businesses. Employee information can be easily found here, along with details such as company size and revenue.
Job Postings
Job postings can offer insight into the direction a company is expanding in, or their particular area of interest. For example, if a company is advertising the posts of two more designers, it’s a safe bet that they’re either looking to improve their current product or they are creating a new one. This information can then influence how you perceive the company as a competitor or supplier, which influences how you’ll interact with them.
Company Data Quality Assessment
To assess the quality of company data, you need to evaluate its accuracy, recency, relevancy to you, and avoid any incomplete data.

Many factors can impact the quality of a database and it is for this reason that you should always ask the data provider to supply you with a sample data set so that you can analyze the data and test it out in your intended use case.
Here are some more details on the factors you should look out for:
Accuracy
First of all, it is important to check if the data that you are considering has high accuracy. If the data contains false information it is going to waste the effort of your sales and marketing teams.
There can be many reasons for inaccurate data in a database, although, it is often the result of flaws in sources and collection methods.
Recency
The variables of a company are constantly in flux: revenue changes from quarter to quarter; new products are released; employees can change jobs or transfer to different branches; and new branches may be established.
At times, sudden market changes can affect the value of the company drastically. Similarly, companies often go on a hiring streak and get a flux of new employees in a short time period. Therefore, it is important to ask if your company database is updated regularly enough to include information from these changes.
Relevancy
The database that you are looking for needs to be relevant to your business. While all the entries present in the database might be from your industry they may not be from the niche or location in which you are looking to market your product.
Moreover, a company may not be ready to be engaged and, if you can find that out before purchasing data, this can save you time and effort.
Volume
You need to ensure that the data you’re buying is comprehensive. This is especially true if your project entails at-scale outreach and B2B lead generation. For such use cases, you probably need a database of 100 companies or more. Before purchasing company data, always check with the provider the volume of company records they have.
Likewise, it’s worth asking whether each company record is as detailed as the next. Even if the company statistics database includes thousands of records, there may be some variation between completion of these records. For example, it’s often easier to pull statistics on companies in certain countries than others.
High quality database provider companies will be able to offer data of any company in your target geography or industry. Which leads us to the final aspect of company data quality assurance: missing data.
Missing Data
A company database of high quality will have very few missing fields and all company data for the firms you’re looking to target. A poor quality database with many missing fields will create more work for your teams in the long run.
This is because if there are incomplete fields in a database, your marketing team or sales team would have to do the extra work on their end to fill in the missing details.
Ensure the company data you’re looking to buy contains all the information you need to avoid this potential drawback.
How is Company Data Priced?
The final step is ensuring you get company data at a price and pricing model which suits you. There are various factors that influence the cost of a company database. These are mainly dependent on what you are looking for. For example, if you need a database with more depth and width, it is going to cost you more.
It is not only the quantity of data that determines the price tag of a company database. The quality of the data is also very important in determining its price. A database of high quality is going to cost you more, whereas, a database of low quality can be very cheap to acquire. The difference in prices among the data of various qualities is substantial.
It is also important to consider that if you are choosing a cheaper data of poor quality, you will have to make up for it with your sales and marketing teams consuming extra hours to fill in the missing information or correct the inaccurate fields.
Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate whether you will find it cheaper to spend more on data of high quality or you would prefer cheaper data and spending more on work hours of your sales and marketing teams.
Other factors like the industry you work in can also affect the price of company data. For example, data can be hard to collect in certain industries where there are more restrictions. In such cases, you will have to shell out more for a limited database.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Factors Determine the Quality of Company Data?
The quality of company data is determined by its accuracy, freshness, and attributes, such as industry, revenue, and employee count. High-quality data is validated and regularly updated, reducing the likelihood of outdated or incorrect records. We recommend verifying with the provider you choose the update frequency and validation methods so that you’re accessing reliable and actionable insights.
How Accurate is Company Data?
Accuracy in company data often refers to how closely the data reflects real-world business attributes, like revenue figures or employee counts. Top datasets achieve accuracy rates above 90% through rigorous verification. For applications like competitive benchmarking or lead generation, we suggest opting for data that has a high degree of detail and cross-referenced verification for reliable results.
How is Company Data Secured?
Our providers secure data with encryption, and access is often governed by compliance with standards such as GDPR. When choosing a provider, we suggest inquiring about their data protection protocols to ensure full compliance with privacy regulations and mitigate security risks.
How is Company Data Delivered?
Company data is available in formats like .csv, .json, or through APIs. Providers commonly offer delivery via cloud storage (e.g., S3 buckets) or real-time API access. For seamless setup, we recommend starting with .csv files if you’re testing the data, then scaling to APIs as integration needs grow.
How Much Does Company Data Cost?
Pricing varies based on factors like data volume, coverage, and frequency of updates. Company data can be accessed through one-off purchases, monthly or yearly subscriptions, or usage-based API models. We suggest trying out free samples (if available on Datarade) to ensure the data aligns with your needs before committing to a larger investment.
What Geographic Areas Are Covered by Company Data?
Most company data providers offer global coverage, including detailed profiles for companies across North America, Europe, Asia, and beyond. Some datasets span more than 200 countries. If you’re targeting specific markets, check the provider’s coverage details, and we recommend opting for datasets that offer granular data within the regions you’re focused on.
Can Company Data Be Integrated With Other Tools?
Absolutely! Company data is generally designed for integration with CRM, BI tools, and analytics platforms. Most providers offer compatibility via APIs or standard formats like .csv for onboarding. Before purchasing, we suggest confirming that the data format is compatible with your existing systems.
Can I Request Custom Company Data?
Yes, custom company data requests are often available to fit unique requirements. Custom options might include filtering data by specific industries or geographies. Pricing for custom requests can vary, so we recommend discussing your specific needs with the provider for a tailored solution.
What Types of Company Data Are Available on Datarade?
Datarade offers a wide range of company data types, including basic firmographic data (industry, size, location), financial metrics, employee details, and technology stack information. If you’re exploring company data for the first time, we suggest starting with general firmographic data and scaling up to more specific datasets as your needs evolve.





